Head Injury
What is a head injury?
Head injuries, referred to as traumatic brain injury (TBI) are one of the most common causes of death and long term disability. It is most commonly caused by Road traffic accidents. Sports injuries, self falls or inflicted trauma like assault can also cause head injury. The injury can be mild as a bump, bruise, or cut on the head, or severe with skull fractures, internal bleed and blood clot or a diffuse brain injury. Hence it forms a very wide spectrum and has to be dealt with utmost seriousness and care. Head injuries are increasing in number among old people as they tend to slip and fall due to imbalance.
Head injury is a potential threat to life and wellbeing and the prognosis depends on the site and extent of the injury. Hence need prompt evaluation and management. The following are some of the different types of head injuries
Skull fracture
A skull fracture is a break in the skull bone. There are four major types of skull fractures, including the following:
- Linear skull fractures. This is the most common type of skull fracture where there is a break in the bone, but the bone itself is not displaced. Usually, no interventions are necessary if occurring in isolation.
Depressed skull fractures. This type is much more severe type of fracture which may be associated with injury to brain. It may be seen with or without an open wound in the scalp. Here a part of the skull is sunken and may be broken into pieces which can injure the brain below. This type of skull fracture may require surgical intervention, depending on the severity, to help correct the deformity.
Diastatic skull fractures. These are fractures that occur along the suture lines in the skull where normal suture lines are widened. This is common in children seen between the bones before fusion.
Base of skull fracture. This is the most serious type of skull fracture, and involves a break in the bone at the base of the skull. Patients will have bruises around their eyes and or behind their ear and is often associated with severe head injury. They may be associated CSF leak due to tear in protective layer of brain called Dura or at times vascular injuries. These patients usually require admission, close observation and at times surgical repair.

Concussion
A concussion is an injury to the head area that may cause instant loss of awareness or alertness for a few minutes up to a few hours after the traumatic event. This needs hospitalization and observation. No surgical intervention required. Sometimes patient will develop memory disturbances, headache and behavioral changes after concussion which usually improves with time. This is called post concussion syndrome.
Intracranial hematoma (ICH)
The different types are classified by their location in the brain. These hematomas are associated with severe head injury and can be life threatening. The different types of ICH include the following:
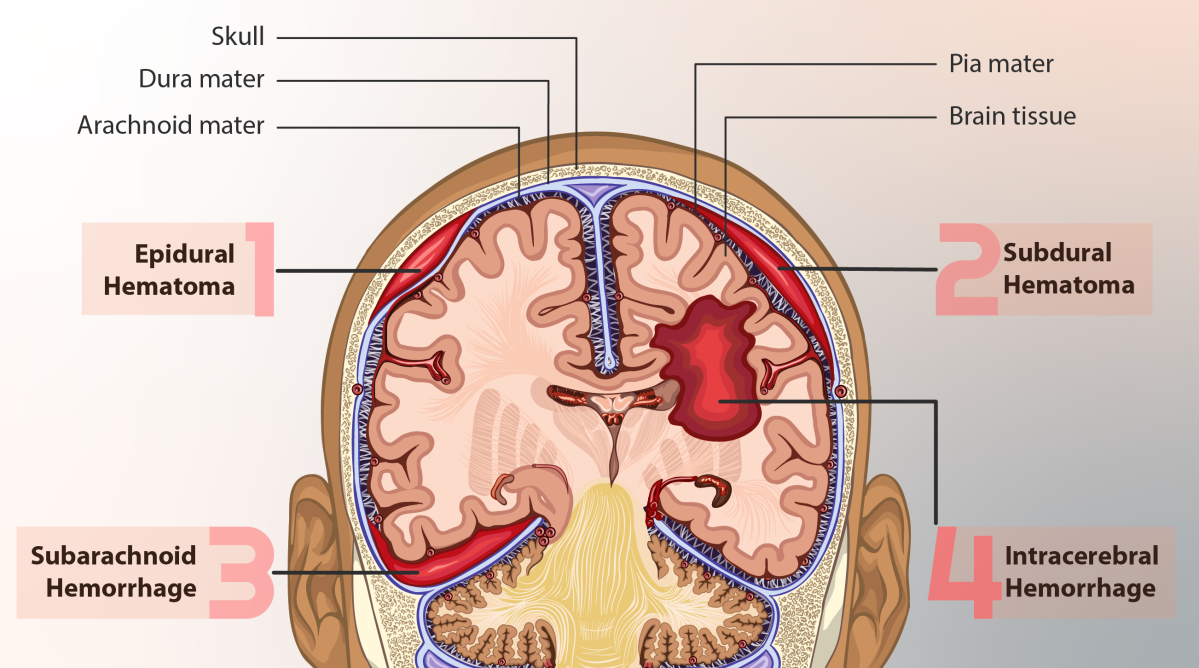
Epidural hematoma. Epidural hematomas occur when a blood clot forms between the skull and the protective tough covering of the brain, dura. Common in RTAs and Sports injuries. Epidural hematomas are usually associated with a skull fracture. Close monitoring is required and might need surgical evacuation to save life at times.
Subdural hematoma. Subdural hematomas occur when a blood clot forms underneath the dura, but outside of the brain surface. Usually caused in severe trauma which can lead to These can form from a tear in the veins on brain or from a cut on the brain itself. They are sometimes, but not always, associated with a skull fracture.
Contusion or intracerebral hematoma. A contusion is a bruise to the brain itself. A contusion causes bleeding and swelling inside of the brain around the area where the head was struck or away at the opposite side where the brain is rubbed against after injury. Associated with severe head injury, skull fractures or sub dural bleeds this requires prompt management. Bleeding that occurs inside the brain itself (also called intraparenchymal hemorrhage) can sometimes occur spontaneously. The most common causes are long-standing, high blood pressure in older adults, bleeding disorders in either children or adults, or the use of medications that cause blood thinning in certain illicit drugs.
Diffuse axonal injury (DAI). These injuries are most dangerous but common and are usually caused by shaking of the brain back and forth, which can happen in car accidents, from falls or shaken baby syndrome. Diffuse injuries can be mild, such as with a concussion, or may be very severe, as in diffuse axonal injury (DAI). In DAI, the patient may remain in coma for a long time and require neuro critical care management and rehabilitation. It is one of the causes of long term disability from brain injury.
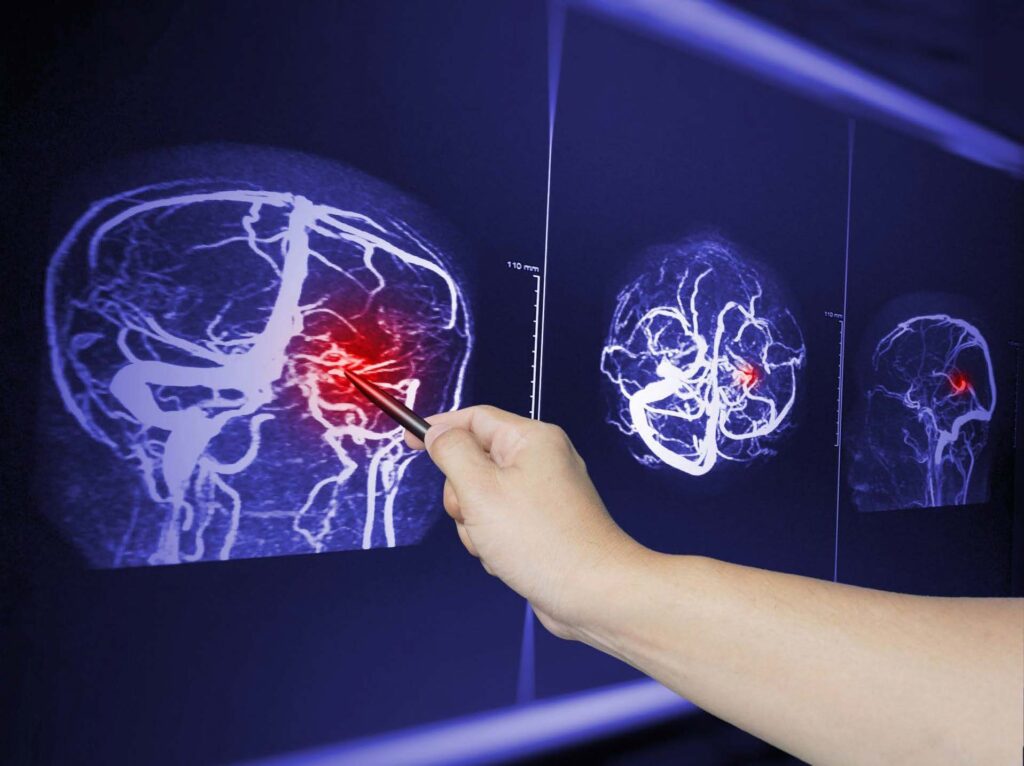
Head injury Work up
Many times head injury also affects other parts of the body and is called polytrauma. This requires not only complete neurological evaluation but the entire emergency care team needs to work in unison to assess and manage these patients.
Radiological imaging such as Computed tomography scan ( CT scan) is the diagnostic imaging procedure of choice. This helps in understanding the injury types and extends and helps in further management.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a much sophisticated investigation but not commonly used after a trauma. It has special usage when we suspect diffuse injury to brain which cannot be picked up by a CT Scan.
Treatment Options
Many patients can be managed as outpatients. But some need admission in ICU and neuro monitoring. Medications are given to many to reduce swelling of brain. But if there are blood clots inside the brain or fractures which needs correction, surgery is warranted.
Lifelong considerations for a person with a head injury
The key is to promote a safe environment for children and adults and to prevent head injuries from occurring in the first place. The use of seat belts when riding in the car and helmets (when worn properly) for activities, such as bicycle riding, in-line skating, and skateboarding may protect the head from sustaining severe injuries.
Persons who suffer a severe brain injury may lose muscle strength, fine motor skills, speech, vision, hearing, or taste function, depending on the brain region involved and the severity of brain damage. Long- or short-term changes in personality or behavior may also occur. These persons require long-term medical and rehabilitative (physical, occupational, or speech therapy) management.
The extent of the person’s recovery depends on the type of brain injury and other medical problems that may be present. It is important to focus on maximizing the person’s capabilities at home and in the community. Positive reinforcement will encourage the patient for better outcomes.

