Neurological investigations
Common Neurological symptoms
These tests are also important for management, checking the progress of treatment, and for further follow-ups.
We use a number of tests for evaluating and confirming the diagnosis.
Most commonly used tests are as below
Blood Investigations
Helps in identifying Metabolic causes of neurological illnesses. Some of the common tests are Complete Blood count, Vit B12, Vit D3, Serum electrolytes, Renal and Liver function tests, coagulation factors, Auto immune panels, Viral markers, bacteriological, fungal and viral genomic tests etc.
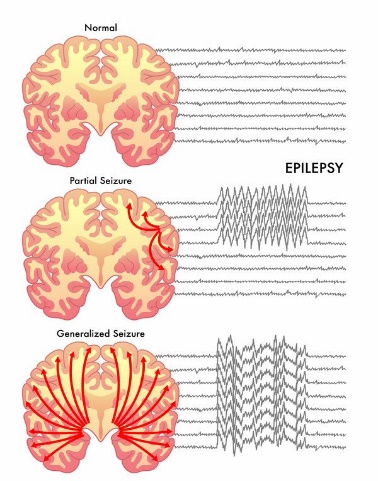
Electroencephalogram
This test records the brain’s continuous, electrical activity through electrodes attached to the scalp. Used very commonly for seizure and epilepsy evaluation. EEG report helps in identifying types of epilepsy syndromes and aid in further management and follow ups.
Cerebral spinal fluid analysis (also called spinal tap or lumbar puncture)
This test takes a sample of cerebrospinal fluid from the lumbar sub arachnoid space for various testing, commonest to rule out infections of the brain. Tumour cells and certain tumor markers are also found in neural cancers.
Neuro Imaging studies: Corner stone in neurological surgical practice
X rays
X-rays help us to understand the cranial vault and spine disease conditions like degenerative diseases, congenital diseases, and metabolic syndromes. However plain radiographs are not very helpful to pinpoint the diagnosis as a single modality and are being sidelined by other sophisticated imaging techniques like CT and MRI for accurate diagnosis.
CT Scan
One of the common, fast,economical and easily available imaging investigation for neuro evaluation. CT scan shows detailed images of brain, bones, muscles, fat, and even blood supply to rain. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays. As technology developed spiral CTs can take very quick scansand are highly capable with post processing stations to give a very detailed 3D imaging of the bone and blood vessels which help us in taking decisions of further management. However, CT scans have limitations the resolution of brain is limited and is harmful to body due to radiation if done in excess.
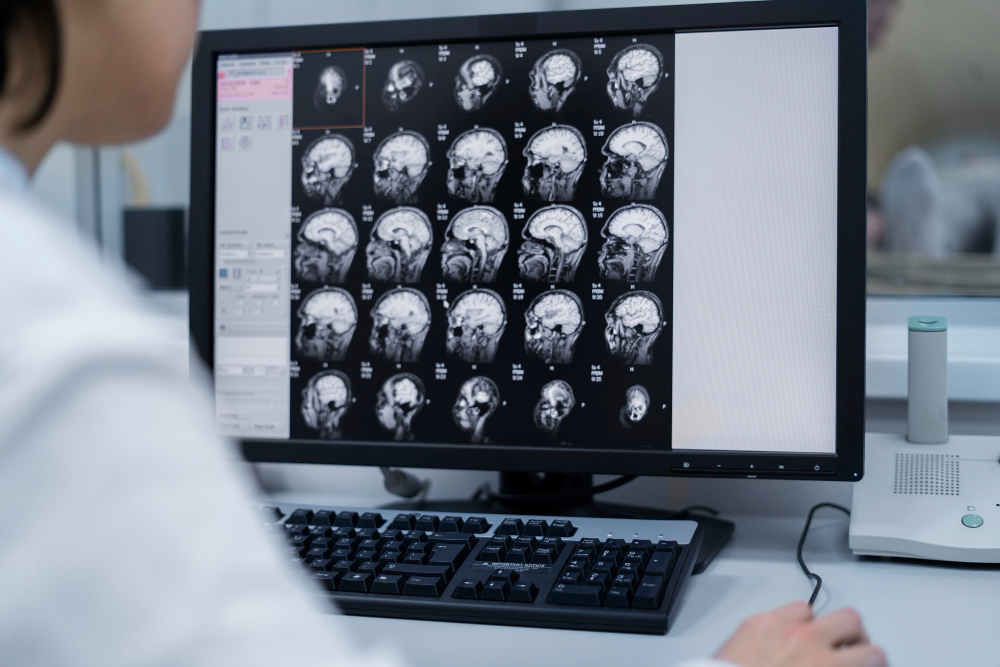
MRI.
This test uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body. Advantages are it gives a very detailed anatomical imaging with excellent image resolution which helps in differentiating various types of brain pathologies and helps us to take decision on diagnosis and treatment. Also MRI has no radiation exposure so can be repeated many times. The only disadvantage is that it cannot be use in patients with some metallic implants in the body and the study takes a long time to complete. Also many patients feels claustrophobic inside an MRI machine. MRI has many advanced functionalities which can help us to identify the structure and function of the brain in great detail. A very valuable tool indeed.
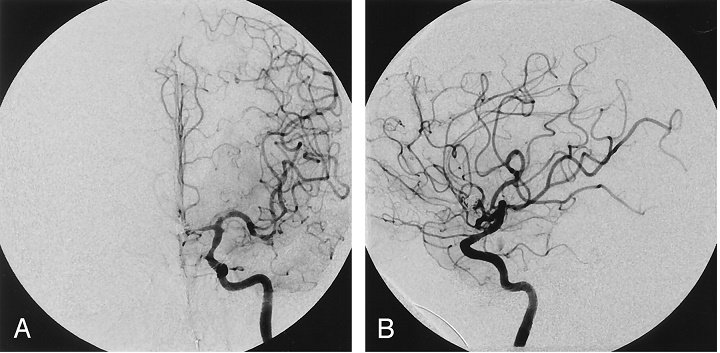
Digital Subtraction Angiography and CT angiogram
This test provides an image of arteries and veins going to and through the brain. Excellent for vessel wall imaging and identifying pathologies of the blood vessels and also seeing the flow of blood. Very important for the assessment of Aneurysms, AV malformations, Occlusions, thrombus formation, etc. The advantage of DSA is intervention can also be done if required when DSA is being done whereas CT angiogram is primarily for diagnosis.
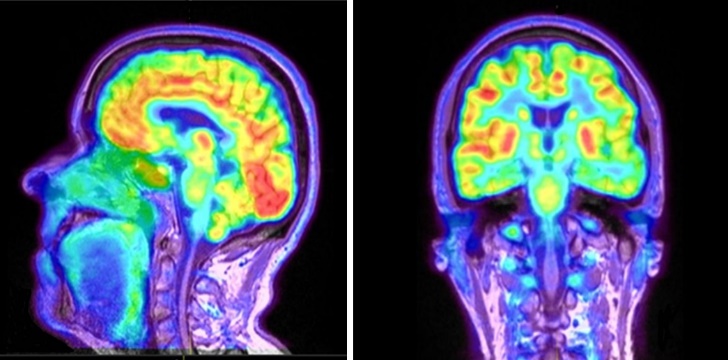
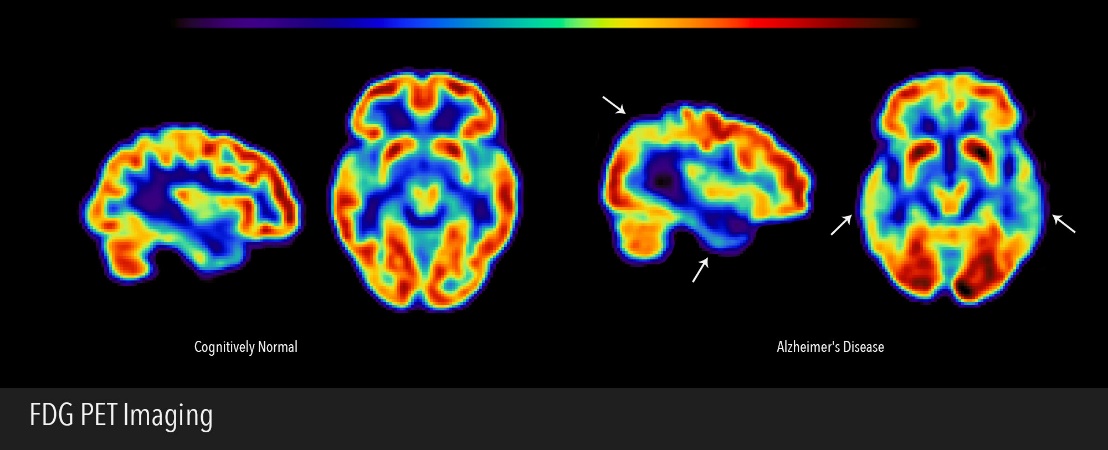
Positron emission tomography scan
This computer-based imaging test provides a picture of the brain’s functional activity rather than its structure by measuring levels of an injected substance with a tracer molecule, most often glucose.
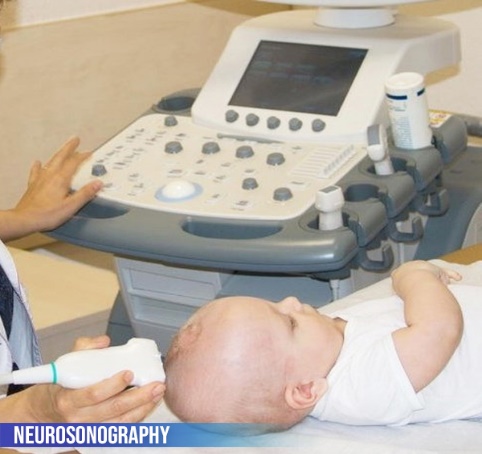
Neurosonography and Doppler sonography
This test uses high-frequency sound waves to evaluate structures of the brain and spinal cord and a computer to create images of neural structures, blood vessels, and flow patterns. Ultrasound of the brain is done in the first few months of life while the infant’s fontanels are open to see inside the brain. There are many situations where blood flow patterns and flow velocity can be affected, like in cerebral vasospasm. USG studies are simple, safe, and fast. However, the accuracy is not much and is operator-dependent. Hence reserved for only certain occasions, esp in newborns and infants.
Electro-diagnostic tests
These include electromyography and nerve conduction velocity. These studies evaluate and diagnose disorders of the nerves, muscles, and motor neurons. Electrodes are inserted into the muscle, or placed on the skin overlying a nerve, muscle, or muscle group, and electrical activity and muscle response are recorded. They are routinely monitored during surgical procedures apart from commonly used for studying nerve and muscle conduction.
Evoked potentials
This test uses high-frequency sound waves to evaluate structures of the brain and spinal cord and a computer to create images of neural structures, blood vessels, and flow patterns. Ultrasound of the brain is done in the first few months of life while the infant’s fontanels are open to see inside the brain. There are many situations where blood flow patterns and flow velocity can be affected, like in cerebral vasospasm. USG studies are simple, safe, and fast. However, the accuracy is not much and is operator-dependent. Hence reserved for only certain occasions, esp in newborns and infants.